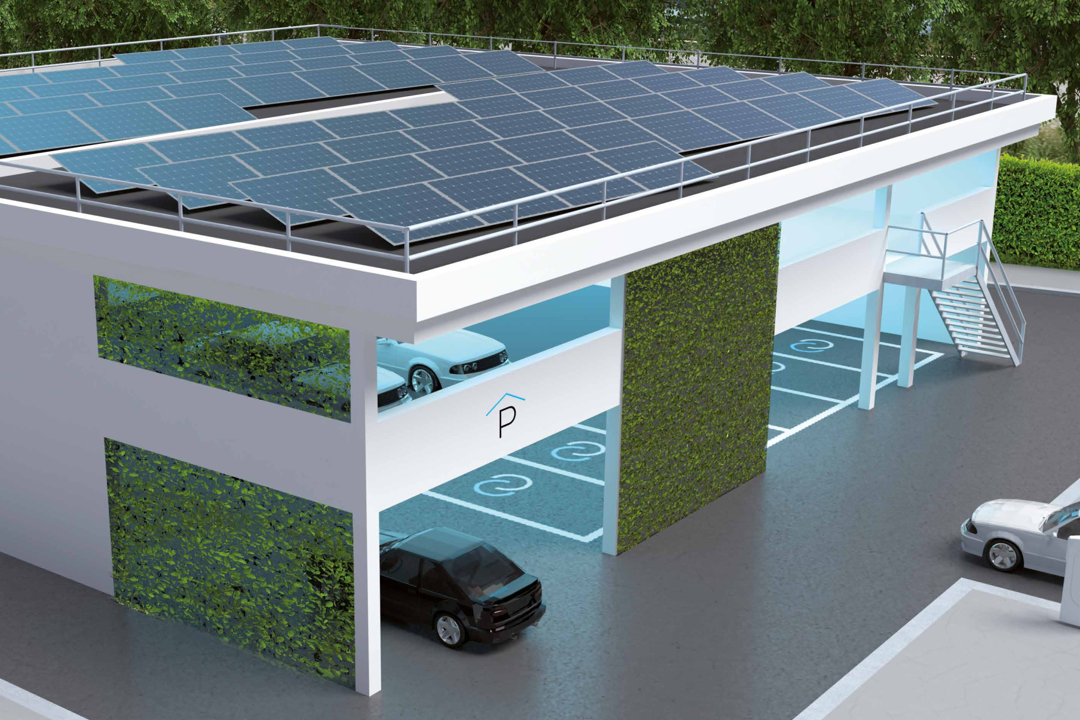
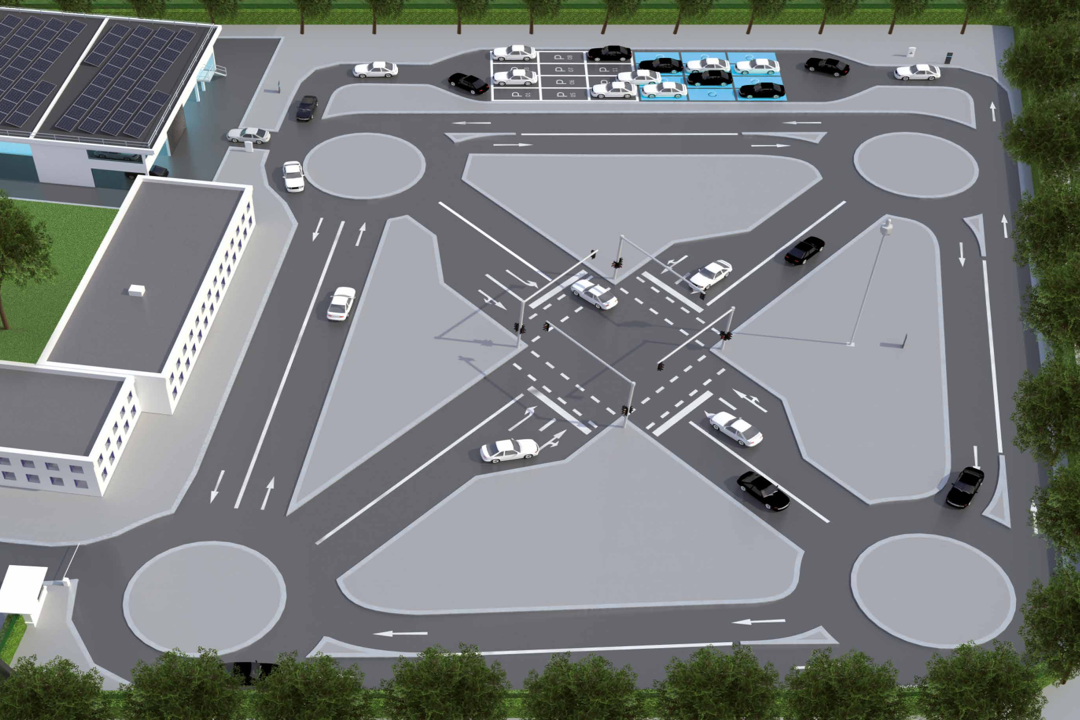
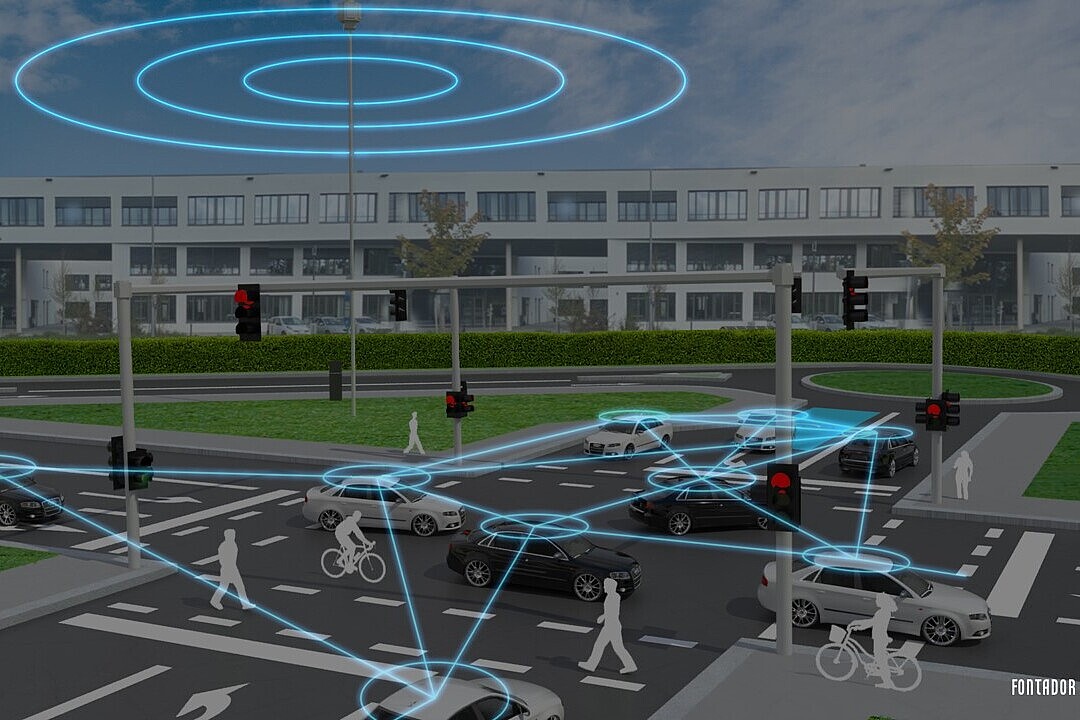
Test Intersection
At the heart of the test field is an intersection equipped with the necessary infrastructure, including traffic areas, a traffic light system (LSA), sensors, and V2X communication. The test intersection allows automated and connected vehicles (AVF) to be tested and validated in a controlled environment before the developed vehicle control algorithms are evaluated, tested, and deployed in real traffic. The AI algorithms, models, and datasets used will be analyzed, and their compliance with standards will be verified using a proprietary data analysis tool (SafeAI).
The traffic areas are complemented by an intelligent, variably controlled, movable traffic light system with open interfaces and comprehensive detection sensors for capturing and accurately determining the positions of all road users (including non-connected pedestrians and cyclists).